I still find Burp Suite the best tool for web-related penetration testing, and assessing Android applications are no exception. In the past, I used my phone with iptables, but lately – especially since the emulator supports using the host OpenGL for graphics – I started to prefer the emulator.
First of all, setting an emulator-wide proxy is really easy, as Fas wrote,
all I needed was the -http-proxy command line argument. Because of this, I
had to start the emulator from command line – I've only used the GUI provided
by android before. I looked at the output of ps w for hints, and at first,
I used a command line like the following.
$ tools/emulator64-arm -avd Android17 -http-proxy http://127.0.0.1:8081
emulator: ERROR: Could not load OpenGLES emulation library: lib64OpenglRender.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
emulator: WARNING: Could not initialize OpenglES emulation, using software renderer.
Since using the Android emulator without hardware rendering would've been like
using Subversion after Git, I looked into the matter and found that I just had
to set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH path to the tools/lib subdirectory of the SDK.
Now I could intercept various TCP connections using Burp, but in case of SSL
connections, certificate mismatch caused the usual problem.
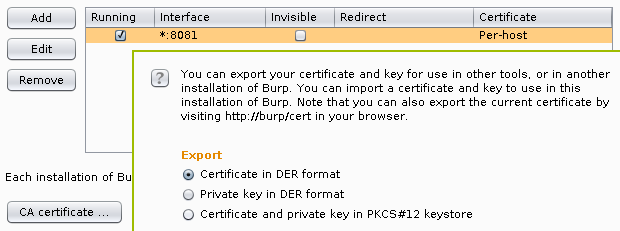
Luckily, Burp provides really easy ways of exporting the its root CA
certificate in the last few releases, I chose to export it into a DER file by
clicking on the Certificate button on the Options subtab of the Proxy
tab, and selecting the appropriate radio button as seen below.
Android 4.x stores root CA certificates in system/etc/security/cacerts/ in
PEM format, so running the following command gives a chance to review the
certificate before adding and the output can be used directly by Android.
$ openssl x509 -in burp.cer -inform DER -text
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number: 1296145266 (0x4d419b72)
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=PortSwigger, ST=PortSwigger, L=PortSwigger, O=PortSwigger, OU=PortSwigger CA, CN=PortSwigger CA
Validity
Not Before: Jan 27 16:21:06 2011 GMT
Not After : Jan 22 16:21:06 2031 GMT
Subject: C=PortSwigger, ST=PortSwigger, L=PortSwigger, O=PortSwigger, OU=PortSwigger CA, CN=PortSwigger CA
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public-Key: (1024 bit)
Modulus:
00:a0:c2:98:2b:18:cf:06:42:4a:7b:a8:c9:ce:ab:
1d:ec:af:95:14:2a:dd:58:53:35:9d:68:18:86:a5:
3a:84:6e:6c:32:58:11:f3:d7:bf:b4:9e:29:d2:dc:
22:d2:7f:23:36:16:9d:10:c4:e5:4c:69:55:4d:95:
05:9f:9b:f8:33:37:8d:9f:d0:23:0f:61:d4:53:d7:
40:fd:da:6d:f0:04:75:2c:ef:75:77:0a:4a:8c:34:
f7:06:6b:4e:ea:58:af:a7:89:51:6b:33:a2:89:5c:
6b:64:cb:e6:31:a7:7f:cf:0a:04:59:5b:a4:9e:e3:
96:53:6a:01:83:81:2b:0b:11
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
FE:2F:6C:CD:EB:72:53:1E:24:33:48:35:A9:1C:DC:C7:D6:42:6F:35
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:TRUE, pathlen:0
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
1e:f0:92:13:bd:05:e8:03:33:27:72:3d:03:93:1e:d9:d6:cc:
f0:bd:ae:e2:a3:8f:83:e0:65:5e:c7:03:9d:25:d4:d2:8f:6e:
bc:3e:7d:5c:28:2d:b3:dd:c0:8b:8e:60:c5:a8:8c:26:dc:19:
50:db:da:03:fb:39:e0:72:01:26:47:a7:ea:c4:58:f5:c9:71:
bf:03:cd:af:16:07:6d:a5:36:72:4c:b5:8d:4f:86:4a:bc:60:
1c:01:62:eb:e5:48:a0:83:c6:1c:ea:b9:36:d6:b1:f1:de:e6:
19:4a:2a:76:7e:d3:d2:39:70:64:a3:63:ce:89:da:2e:7d:17:
ff:52
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIICxDCCAi2gAwIBAgIETUGbcjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADCBijEUMBIGA1UEBhML
UG9ydFN3aWdnZXIxFDASBgNVBAgTC1BvcnRTd2lnZ2VyMRQwEgYDVQQHEwtQb3J0
U3dpZ2dlcjEUMBIGA1UEChMLUG9ydFN3aWdnZXIxFzAVBgNVBAsTDlBvcnRTd2ln
Z2VyIENBMRcwFQYDVQQDEw5Qb3J0U3dpZ2dlciBDQTAeFw0xMTAxMjcxNjIxMDZa
Fw0zMTAxMjIxNjIxMDZaMIGKMRQwEgYDVQQGEwtQb3J0U3dpZ2dlcjEUMBIGA1UE
CBMLUG9ydFN3aWdnZXIxFDASBgNVBAcTC1BvcnRTd2lnZ2VyMRQwEgYDVQQKEwtQ
b3J0U3dpZ2dlcjEXMBUGA1UECxMOUG9ydFN3aWdnZXIgQ0ExFzAVBgNVBAMTDlBv
cnRTd2lnZ2VyIENBMIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCgwpgrGM8G
Qkp7qMnOqx3sr5UUKt1YUzWdaBiGpTqEbmwyWBHz17+0ninS3CLSfyM2Fp0QxOVM
aVVNlQWfm/gzN42f0CMPYdRT10D92m3wBHUs73V3CkqMNPcGa07qWK+niVFrM6KJ
XGtky+Yxp3/PCgRZW6Se45ZTagGDgSsLEQIDAQABozUwMzAdBgNVHQ4EFgQU/i9s
zetyUx4kM0g1qRzcx9ZCbzUwEgYDVR0TAQH/BAgwBgEB/wIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0B
AQUFAAOBgQAe8JITvQXoAzMncj0Dkx7Z1szwva7io4+D4GVexwOdJdTSj268Pn1c
KC2z3cCLjmDFqIwm3BlQ29oD+zngcgEmR6fqxFj1yXG/A82vFgdtpTZyTLWNT4ZK
vGAcAWLr5Uigg8Yc6rk21rHx3uYZSip2ftPSOXBko2POidoufRf/Ug==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
As rustix wrote, the file name needs to be the the hash of the subject of the certificate, in case of the above certificate, it can be calculated as the following.
$ openssl x509 -noout -subject_hash_old -inform DER -in burp.cer
9a5ba575
Now all we need is to upload the file using adb.
$ adb push burp.cer /system/etc/security/cacerts/9a5ba575.0
failed to copy 'burp.cer' to '/system/etc/security/cacerts/9a5ba575.0':
Read-only file system
The error message was fairly straightforward, /system is mounted read-only,
all we need to do is remounting it in read-write (rw) mode.
$ adb shell
root@android:/ # mount -o rw,remount /system
root@android:/ # ^D
$ adb push burp.cer /system/etc/security/cacerts/9a5ba575.0
failed to copy 'burp.cer' to '/system/etc/security/cacerts/9a5ba575.0':
Out of memory
That's a tougher one, but easily solveable by resizing the system partition
using the emulator command line argument -partition-size. With this change as
well as the library path for OpenGL, the full command line looks like the
following (of course, 64 should be removed if you're using a 32-bit OS).
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=tools/lib/ tools/emulator64-arm -avd Android17 \
-http-proxy http://127.0.0.1:8081 -partition-size 512
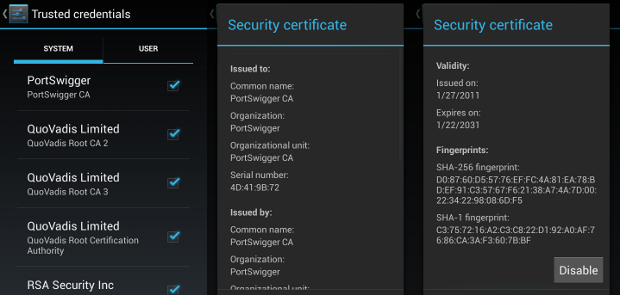
Since restarting the emulator wiped my changes from /system, I had to upload
the certificate again, and finally, it appeared in the list of system
certificates.
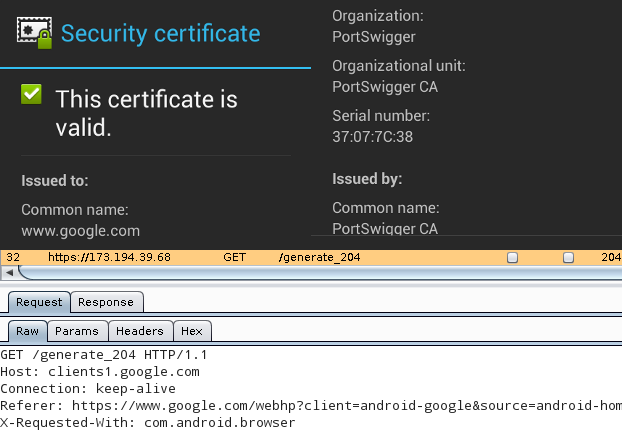
This being done, all applications using SSL/TLS connections (except for those
that do certificate pinning) will accept the MITM of Burp, as it can
be seen below with Google as an example. The top half is the certificate
viewer of the Android web browser, stating that Portswigger issuing a
certificate for www.google.com is perfectly valid, while the bottom half
is the Burp Proxy window, showing the contents of the HTTPS request.